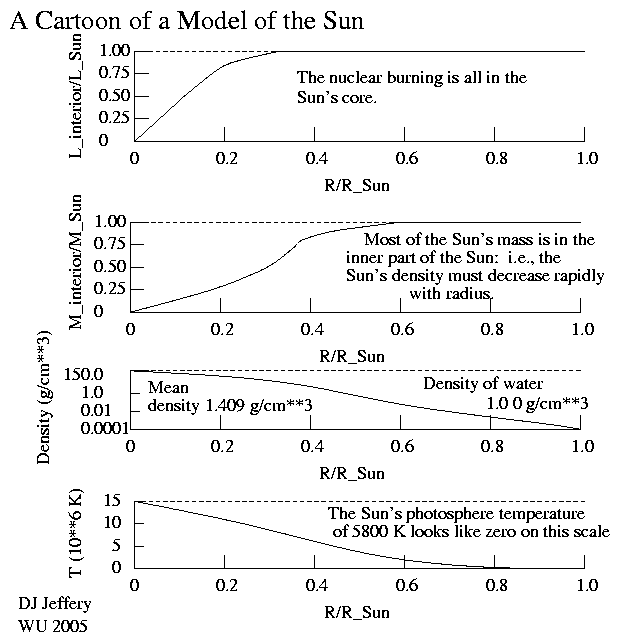
Caption: Cartoon of a stellar structure model (i.e., interior stellar structure model) of the Sun (CK-263) showing the "runs" (i.e., distributions) of interior luminosity, interior mass, density, and temperature as functions radius in units of the solar radius R_☉ = 6.957*10**5 km = 109.1 R_⊕ = 4.650*10**(-3) AU.
Features:
- Stellar structure models
must be calculated using
numerical methods
on the computer from the
4 equations of stellar structure.
There are NO
analytic solutions.
- Usually
for stellar structure models,
the outer boundary conditions
for density
and temperature
are set to zero
since they are so small that are negligible for the
interior structure and can only be determined
to any accuracy/precision
by a stellar atmosphere model
in any case.
- Below is a table illustrating the center-to-surface variations in
Sun quantities
radius,
interior luminosity,
interior mass,
density,
temperature,
and pressure.
The surface values are determined by
stellar atmosphere models.
_________________________________ Table: Center and Photosphere Quantities of the Sun _________________________________ Center Photosphere _________________________________ R (m) 0 6.96*10**8 L (W) 0 3.828 *10**26 M (kg) 0 1.98855 *10**30 Density 150 2.18 *10**(-7) (g/cm**3) T (K) 15.7 5772 *10**6 Pressure 2.33 0.827 (Earth *10**11 atmos- pheres) _________________________________References: Cox-342, Wikipedia: Sun._________________________________
- As one can see from the table above and
the plots,
there are vast center-to-surface variations in
Sun
quantities.
In particular, the pressure at the Sun's center is huge as it must be to hold up the Sun against the force of gravity acting on the Sun's own mass (i.e., against the Sun's self-gravity) and trying to collapse Sun.
Note that only the pressure force can support astronomical objects against their own self-gravity for astronomical objects more massive than a small asteroid and unsupported by kinetic energy.
- The Sun's surface temperature
(i.e.,
photospheric temperature)
in the above table is
determined by
Wien's law
by approximating the
Sun as
black-body radiator.
Reversing the calculation, one finds
the solar spectrum
maximum in
the wavelength representation is
λ_max = 2897.7685(51) micron-K / 5772 K ≅ 0.5015 microns which is in the visible range 0.4--0.7 microns.The maximum is, in fact, in the green light band (fiducial range 0.495--0.570 μm) which means there is a lot of green light in the solar spectrum (but NOT that green light dominates the solar spectrum) just where psychophysical response peaks (see file Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) file: human_luminosity_function.html), but the psychophysical response to sunlight is what we call white light. For further discussion of star colors, see file Blackbody file: blackbody_spectra.html#Star Colors.
Image link: Itself.
Local file: local link: sun_model_interior.html.
File: Sun file: sun_model_interior.html.