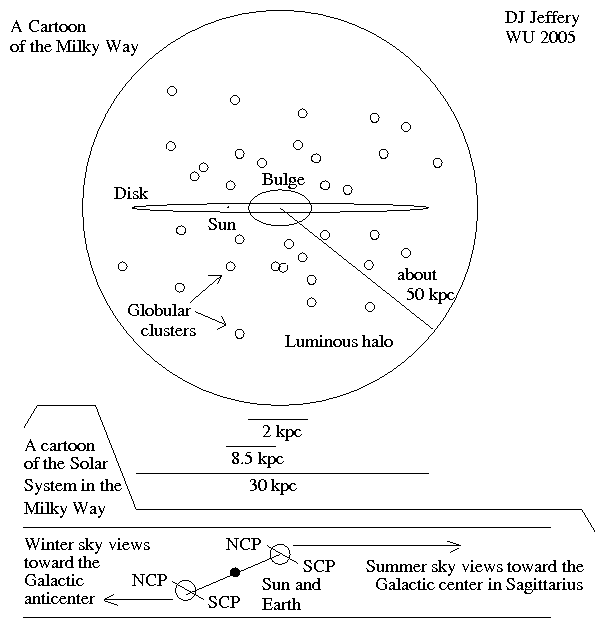
Caption: A cartoon of the Milky Way (AKA the Galaxy)---which is a fairly typical spiral galaxy. Note, the values in the cartoon are somewhat out of date, but are still good enough roughly speaking. Note also, since Milky Way structures have NO sharp edges, sizes are somewhat dependent on the definition used by those assigning the size.
Features:
- The main components of the Milky Way
in outward going order roughly speaking:
Sagittarius A*
(Galactic central black hole,
Milky Way
or Galactic center black hole),
Milky Way center (AKA Galactic center of mass):
distance = 8.122(31) kpc = 26.490(100) kly,
Milky Way bulge: radius ∼ 3 kpc,
Milky Way bar,
Milky Way disk
(Milky Way:
disk diameter ≅ 30 kpc, disk average thickness ≅ 0.3 kpc),
Milky Way spiral arms,
Milky Way globular clusters
(more than 150 are known: see
Wikipedia: Globular clusters;
Wikipedia: List of
globular clusters),
Milky Way halo:
stellar matter radius ∼ 60 kpc,
Milky Way
dark matter halo: radius >∼ 100 kpc ???,
Milky Way mass:
total/dark matter ∼ 10**12 M_☉, stars/gas/dust ∼ 5*10**10 M_☉
≅ 5 % of total.
- Overwhelmingly most spiral galaxies
have obvious
galactic bulges
and galactic disks:
Milky Way is typical of this.
However, they all have rather spherical
galactic halos
(which consist of low-density
baryonic matter
(interstellar medium (ISM),
rather isolated stars,
and globular clusters)
and dark matter).
The galactic halos can extend
much farther than the galactic disks,
but their edges are hard to find since they become invisible as the
baryonic matter gets rarer going
outward.
The distribution and extent of dark matter
in the dark matter halos
is particularly hard to determine since it is entirely invisible so far, except through the effects of its
gravity.
The dark matter halos
(probably rather spherical in general)
may extend out to >∼ 100 kpc from the
spiral galaxy center
and have ∼ 5 -- 20 times ???? the
mass
of all the baryonic matter
in the spiral galaxy.
Computer simulations
based on the Λ-CDM model
give some insight into the
structure of
dark matter halos
insofar as they are realistic.
Stellar streams (made of tidally disrupted dwarf galaxies or globular clusters) in the Milky Way may eventually give direct observational information about the distribution of dark matter in Milky Way dark matter halo (see Eric Hand, Science, 2018oct05, "Sky Rivers").
- See Keywords: Milky Way below or at keywords_milky_way.html:
Local file: local link: milky_way_cartoon.html.
File: Galaxies file: milky_way_cartoon.html.