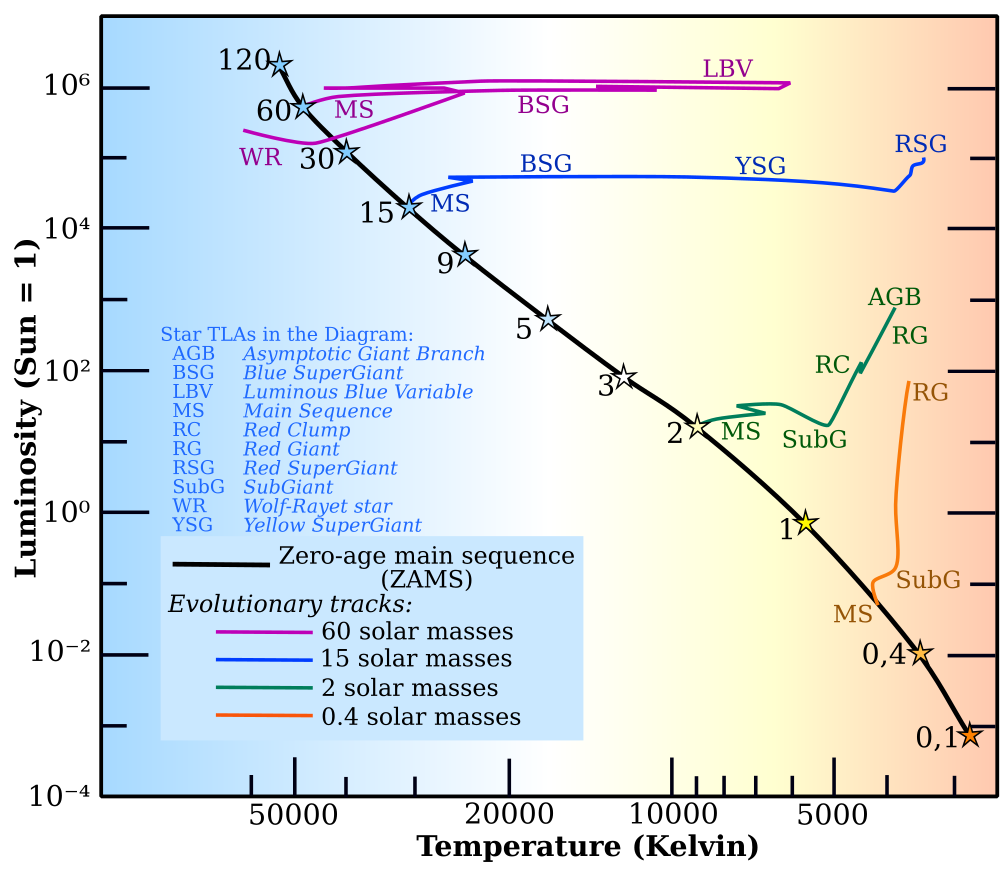
Caption: A Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram showing a representative sample post-main-sequence evolutionary tracks for single stars of various initial stellar masses, all with initial fiducial solar metallicity Z=0.02 and zero angular momentum.
Note the following HR diagram bands:
- AGS = asymptotic giant branch.
- BSG = blue supergiants.
- LBV = luminous blue variable.
- MS = main sequence.
- RC = red clump: The stars in this HR diagram band are cool horizontal branch stars.
- RG = red giant.
- RSG = red supergiants.
- SubG = subgiants.
- WR = Wolf-Rayet star.
- YSG = yellow supergiant.
The evolutionary tracks leave the main sequence mostly moving toward the upper right half of the HR diagram.
So post-main-sequence stars are typically cooler and, except at the high-mass end, brighter than than main-sequence stars.
In understanding stellar evolution, you should always remember the main-sequence rule (local link / general link: star_main_sequence_rule.html).
EOF
For further understanding of
post-main-sequence evolution,
see
Post-main-sequence evolution keywords
below
(local link /
general link: post_main_sequence_keywords.html):
-
EOF
Image link: Wikipedia: File:Stellar evolutionary tracks-en.svg. Local file: local link: star_hr_post_main_sequence.html.
File: Star file: star_hr_post_main_sequence.html.