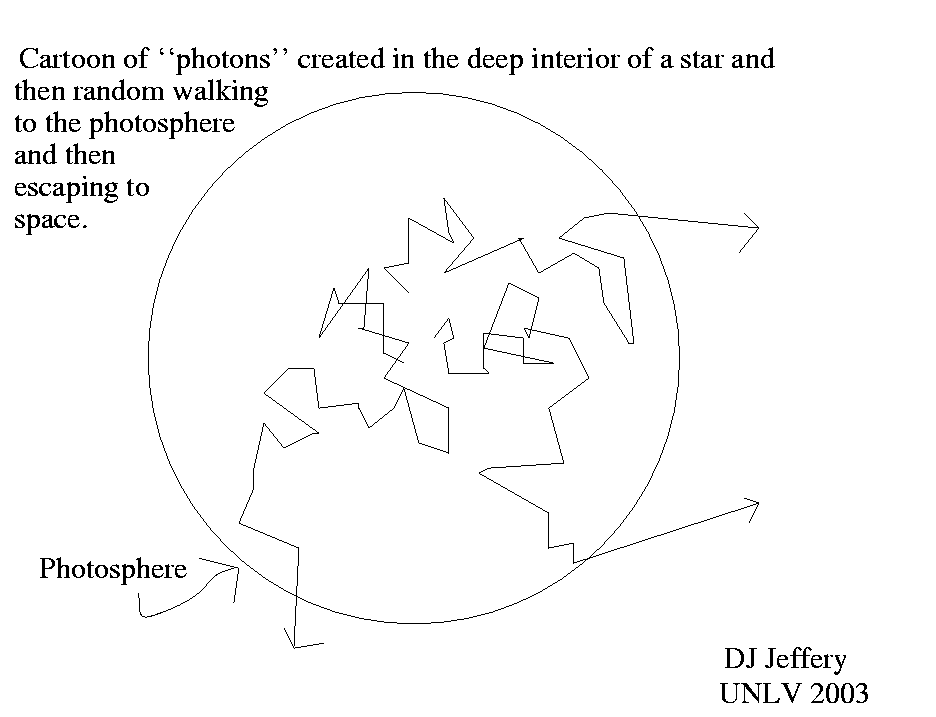
Caption: Cartoon of photons (more realistically, photon packets) executing a random walk from the interior of a star and then escaping from the photosphere.
Recall, stars have NO sharp surface. By surface, we usually mean the photosphere: the surface from which photons escape to infinity about half the time.
Features:
- In gases,
radiative transfer
(i.e, the propagation of
electromagnetic radiation (EMR))
is mainly by a process of
photons
traveling some distance,
being scattered (which means the
photons largely retain their identities)
in a random direction or absorbed with their
energy being eventually converted
to other photons and reemitted in
a random direction.
For scattering, the simplest angular redistribution
probability density
is an isotropic one which is usually a good approximation, but
more complex ones are needed in some cases.
For
absorption/reemission,
an isotropic angular redistribution
probability density
almost always holds.
There are also true sources/sinks for EMR in general.
Between interactions, the photons can be modeled as traveling in straight lines.
The upshot of the aforesaid description is that radiative transfer is by a random walk which becomes fully freestreaming only in the limit of zero opacity which happens beyond the stellar atmosphere which is above the photosphere. The overall motion of individual photons is complex, but in aggregate their behavior can be treated statistically as discussed below. At the macroscopic scale, the cumulative effect of all the random walks is a diffusion process that morphs into freestreaming in the limit of zero opacity.
- In most cases for radiative transfer
random walks,
there are both scattering and
absorption/reemission events.
A single photon usually takes only
a few scattering steps dropping to none sometimes before
an absorption destroys it converting its energy
into heat energy
of matter.
A reemission
converts heat energy
of matter
into new photons.
For real photons, there is
a sort of continuing identity through the scattering process, but
there is NO continuing identity between absorbed and reemitted
photons.
Real photons CANNOT be used in radiative transfer calculations. There are vastly too many of them and their population number varies in a complex way.
However, one can model the radiative transfer by photon packets in a Monte Carlo radiative transfer computer simulation of a random walk. Photon packets, in fact, give the aggregate behavior of large groups of photons on average, capturing both the random walk behavior, the scattering behavior, and the absorption/reemission behavior.
Note:
- The photon packets are indestructible. They are created in the core of a (model) star by heat energy released by nuclear burning and random walk till they escape to infinity near the photosphere or in the stellar atmosphere. Their indestructibility guarantees energy conservation in the radiative transfer calculation.
- The photon packets only change energy due to the Doppler effect. They lose/gain energy during a redshift/blueshift.
- In a scattering event, the photon packets change frequency only slightly in the comoving frame (i.e., the inertial frame moving with medium) due to a very small Compton scattering effect. The frequency change due to the Compton scattering effect only becomes significant as frequency approaches the gamma ray band (fiducial photon energy range 1 kev--∞; fiducial frequency range 2.42*10**17--∞; Hz; fiducial wavelengh range 0--1.24 nm).
- However, the frequency of the photon packets changes radically in absorption/reemission events. The frequency on reemission is distributed according to the thermal state where the absorption/reemission event occurs. Below about the photosphere, this means the frequency on reemission will be distributed according to a blackbody spectrum distribution at the temperature of the absorption/reemission event location. The upshot is the photon packet frequency will be in the X-ray band (fiducial range 0.1--100 Å) in the deep interior and decreases gradually as the photon packet moves outward until at about the photosphere it is in the ultraviolet band (fiducial range 0.01--0.4 μm), visible band (fiducial range 0.4--0.7 μm = 4000--7000 Å), or infrared band (fiducial range 0.7 μm -- 0.1 cm).
- Why do the photon packets
actually move at all on average if they are
random walking?
Well, their average position stays in the zone of initial creation in the star's nuclear burning core, but the distribution of any set of photon packets widens until it's broader than the star. So eventually, all the photon packets will be outside of the star freestreaming to infinity---while their average position stays in the star's nuclear burning core.
Note also that star density falls outward from the center, and so this biases a random walk direction toward the surface region (i.e., photosphere and stellar atmosphere) of a star. The bias is because photon packets have longer steps usually in the lower density directions because of usually lower opacity in those directions.
- The random walk to escape for
photon packets
actually takes a long time.
A rough estimate is of order 10,000 years for a photon packet to go from center to photosphere of the Sun (Shu-90).
Recall from above, NO single photon goes very far in a star. Photons are created and destroyed as energy is propagates outward. But computer simulation of radiative transfer by indestructible photon packets gives the aggregate behavior as aforesaid.
- The direct flight time for a photon from the
Sun's center to the
photosphere surface can
be easily calculated:
t = R_Sun/c ≅ 6.96*10**8 m / ( 3*10**8 m/s ) ≅ 2 seconds .
So the random walk process is relatively slow: 10,000 years compared to 2 seconds for the case of the Sun. - The 10,000 years estimate for the case of the
Sun shows it takes a long time
for certain kinds of changes in the deep interior of
stars
to affect the surface.
However, energy signals do NOT have to rely on radiative transfer. Asteroseismic waves (for the special case of the Sun, these are called helioseismic waves) can travel much faster from center to photosphere of stars (including the Sun) than photon packets random walking though much slower than the vacuum light speed c = 2.99792458*10**5 km/s. Yours truly CANNOT find a source that says how fast at this moment.
Image link: Itself.
Local file: local link: photon_escape.html.
File: Star file: photon_escape.html.