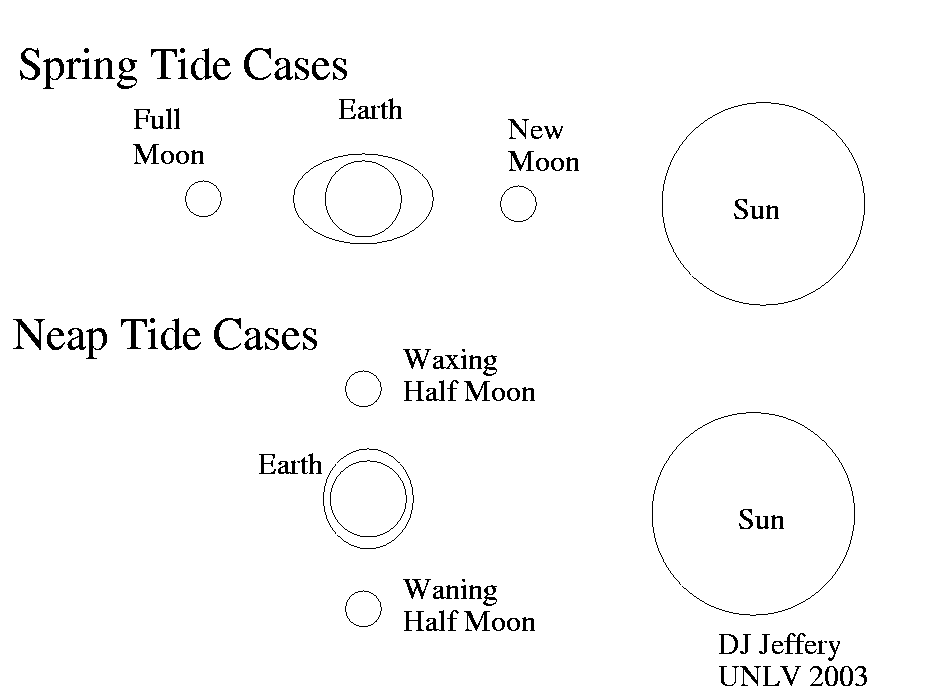
Caption: The tidal forces of the Moon and Sun create the tidal bulges of the World Ocean.
As illustrated, spring tides are the largest tides and neap tides the smallest tides.
Features:
- The tidal force
is the stretching force
due to varying EXTERNAL
gravitational field.
The tidal force is actually a combination of an ordinary force and an inertial forces both of which originate with the EXTERNAL gravitational field. We will NOT go further into this somewhat complex topic.
- The tidal force
combined with the Earth's
self-gravity,
and pressure force,
and centrifugal force gives
the Earth its shape.
- Because the Moon is much closer
than the Sun,
it has a more rapidly varying
gravitational field
and that turns out to dominate over the overall stronger
gravitational field of the
Sun.
Hence the tidal force of the Moon is stronger than that of the Sun.
- When Moon
and Sun are aligned with
the Earth
(i.e., new moon or
full moon),
their tidal forces add and
tides are largest as aforesaid.
These tides are spring tides where "spring" has the meaning of the jump, burst forth, rise, etc.
Coastal storms that coincide with spring tides are particularly dangerous and prone to cause flooding.
- When Moon
and Sun are at
a right angle
as seen from Earth
(i.e., first quarter moon
or
last quarter moon),
their tidal forces counteract each other, but
Moon's wins, but the
tides are smallest as aforesaid.
These tides are neap tides. "Neap is an Old English (AKA Anglo-Saxon) word meaning without the power" (Wikipedia: Range variation: springs and neaps, slightly edited).
- Because of the
Earth's rotation
(counterclockwise
as seen from the north celestial pole (NCP))
relative to the
observable universe
(with period
sidereal day = 86164.0905 s = 0.997269566 days
= 1 day - 4 m + 4.0905 s (on average)),
the tide is continuously deforming
and reforming water bodies.
However, Moon also
orbits the Earth
(counterclockwise
as seen from the north celestial pole (NCP))
relative to the
observable universe
with
mean lunar sidereal month 27.321661547 days (J2000) ≅ 27.32166 days (to 7 digits) ≅ 27.3 days
Thus, the Moon's
rotation partially cancels the
Earth's rotation prolonging the
time between
high tides
to ∼ 12 hours and 25.2 minutes in most locations.
(Wikipedia:
Tide: Principal lunar semi-diurnal constituent).
So sailors have to have
tide tables handy so as to know
when the tides will be and how high/low they
will be.
For example, see Sven
or
Sven.
- As well as the water tide,
there is also an Earth tide---but we never
notice the continents
going up and down by a ∼ 1 meter about twice a day.
There's an atmospheric tide too and furthermore:
-
There is a tide
in the affairs of men,
Which, taken at the flood, leads on to fortune;
Omitted, all the voyage of their life,
Is bound in shallows and in miseries.
-
---
Brutus (85--42 BCE) to
Cassius (before 85--42 BCE),
Act IV, Scene 3
(scroll down ∼ 70 %)
in Julius Caesar (c. 1599),
William Shakespeare (1564--1616).
- See Tide videos below (local link / general link: tide_videos.html).
Local file: local link: tide_earth.html.
File: Mechanics file: tide_earth.html.