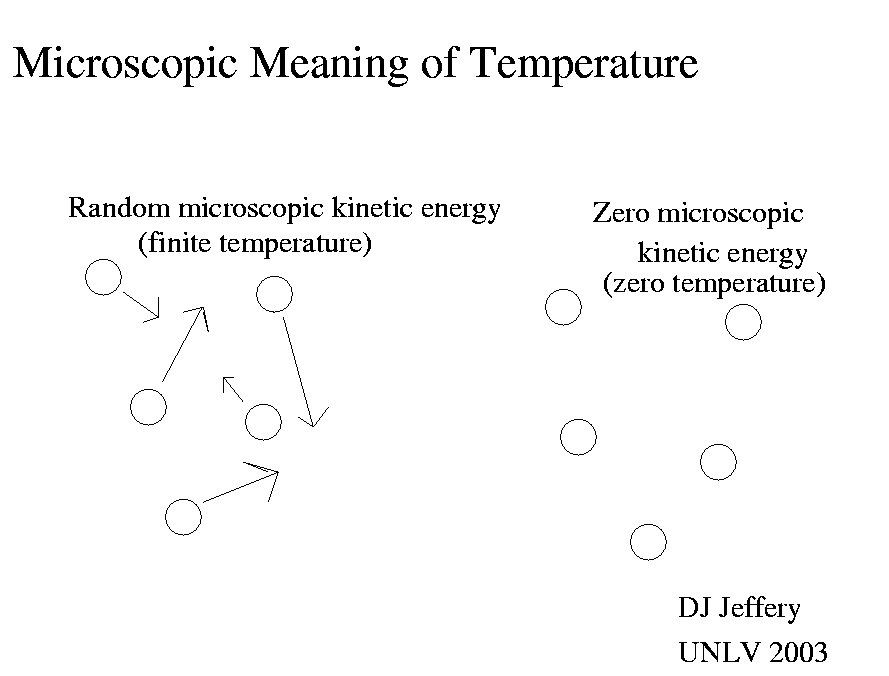
Caption: In classical physics, absolute zero for a gas is reached when all the kinetic energy has been removed from the molecules or atoms in the case of a monatomic gas.
HOWSOEVER, quantum mechanics dictates that there is an irremovable miminum amount of kinetic energy called the zero-point energy.
So in our modern understanding, absolute zero for a gas is reached when you reach the zero-point energy for the molecules or atoms in the case of a monatomic gas.
Credit/Permission: ©
David Jeffery,
2003 / Own work.
Image link: Itself.
Local file: local link: temperature_microscopic.html.
File: Kelvin file:
temperature_microscopic.html.