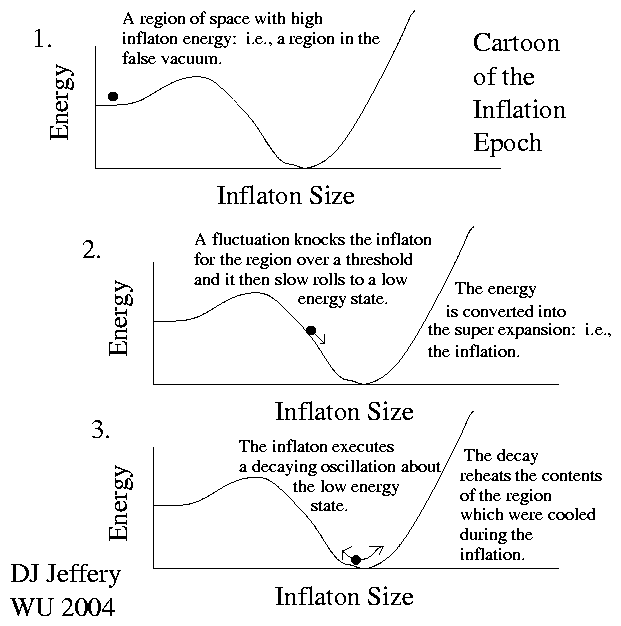
Image 1 Caption: A cartoon of false vacuum decay from the false vacuum to the quantum vacuum state (the "true vacuum").
Note in quantum field theory (the best verified of all physics theories), the vacuum (i.e., quantum vacuum state and the false vacuum if it exists) is NOT passive, empty space, but a seething mess of quantum fluctuations in which virtual particles are constantly popping into and out of existence: these virtual particles are NOT directly observable, but have well verified effects.
- Inflation
(using the term in a broad sense)
is a paradigm: i.e.,
an overall grand theory or
framework theory.
It is the inflation paradigm.
In fact, inflation (using the term in a broad sense), the inflation paradigm, and inflation cosmology are synonyms in many contexts.
In a narrower sense, inflation means the inflation era (cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero of standard Friedmann equation models)
As per usual for many words, context tells you what inflation means precisely.
- Inflation
is most discussed in regard to the
very early
(observable) universe (cosmic time t ⪅ 10**(-12) s from fiducial time zero
of standard Friedmann equation models), but, in fact, it is a general
theory of
observable universe
and some large surrounding
universe.
For definiteness, we will just call that part of the whole universe (i.e., everything that is) where inflation happened to make the observable universe the inflation region.
The inflation region may be coextensive with the whole universe, but we do NOT know and it is NOT required by basic inflation.
Inflation may apply beyond the inflation region and maybe to the whole universe, but we do NOT know and it is NOT required by basic inflation.
Now the whole universe may be eternal and infinite. This is a common way of thinking of the whole universe, but we do NOT know if it is true.
In fact, to theorize about the whole universe requires guidance from known physical theories. Usually, the guidance is that we assume that general relativity, quantum field theory, theory of everything (TOE) (which we do NOT yet have), and thermodynamics (particularly 2nd law of thermodynamics) apply to the whole universe.
If they don't, we may have to fall back on philosophy which may NOT be fruitful: i.e., does NOT lead to any progress.
- To be clear,
inflation
is NOT known to be true, but it is the leading
paradigm for
the origin of the
observable universe.
In fact, inflation has been the leading paradigm for the origin of the observable universe nearly since it was introduced circa 1979 (see Wikipedia: Inflation: History). So it has some staying power.
Note, there are many fascinating physical theories are dismissed or downgraded to just interesting ideas after a short period of time. They have no staying power. But, of course, such physical theories can be revived later if they again become interesting.
- Inflation
is the paradigm in terms of which
most cosmologists think.
However, there are rival physical theories to inflation which we will NOT go into here (see Wikipedia: Cosmic Inflation: Alternatives and adjuncts).
However, there are many particular inflation theories with well specified behavior and parameters, but which of those is right (assuming that inflation is right), we do NOT know.
- Nota bene:
Inflation
and other versions of quantum cosmology
are embedded in the grander
paradigm of
quantum field theory.
Yours truly is often forced to say things like
"quantum field theory
dictates" or
"this seems good to
quantum field theorists".
Yours truly does NOT actually know why
"quantum field theory
dictates"
or why "this seems good to
quantum field theorists".
- Inflation
postulates a force field
called the inflaton
that permeates the
inflaton region at least---and perhaps
well beyond as discussed above.
The inflaton is a quantum field whose specific properties depend on the specific inflation theory considered.
- Image 1 illustrates, in cartoon fashion,
the energy
of the inflaton as a
function
of the inflaton field strength.
The inflaton field strength is a measure of the force the inflaton can exert.
The inflaton field strength is analogous to the field strength of the electromagnetic field which is the cause of the electromagnetic force.
- The inflaton
has a high energy
state called
the false vacuum state
(the local minimum
at the left in
Image 1)
and a low energy
state
called the
quantum vacuum state
(at the global minimum in
Image 1).
The quantum vacuum state
is sort of the "true vacuum" as aforementioned.
The whole region of false vacuum constitutes the false-vacuum universe. The false-vacuum universe is probably a rather bland place where there is NOT much structure.
Basic inflation does NOT specify how extensive the false-vacuum universe is in time and space. But it may be the background state for some or all of the whole universe.
- Occasionally (and basic
inflation
does NOT tells us how often),
a random quantum fluctuation
(and random quantum fluctuations
are a fundamental feature of
quantum mechanics
and quantum field theory)
pushes a region of
the false-vacuum universe
(and it may or may NOT be the
whole universe)
over an energy threshold
and the region transitions to the
quantum vacuum state.
The region is the aforementioned inflation region. and the transition process is called false vacuum decay.
Note, the false vacuum state is a metastable state since it is stable against small perturbations, but NOT against sufficiently large ones AND it is NOT the lowest energy state.
- In inflation,
the inflation region
becomes the observable universe
and presumably some unobservable surrounding
universe
which is much the same as the
observable universe in behavior.
In fact, observable universe and the unobservable surrounding universe (i.e., the inflation region) may be the whole universe (as suggested above) or just a finite region of whole universe called a pocket universe in astro jargon.
- The inflation region
undergoes a super rapid exponential expansion
which is the inflation
of inflation
and can be called
inflation super rapid
exponential expansion.
The inflation super rapid
exponential expansion is much faster than
the universal expansion
of the post
inflation era
(cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero
of standard Friedmann equation models)
in which we live.
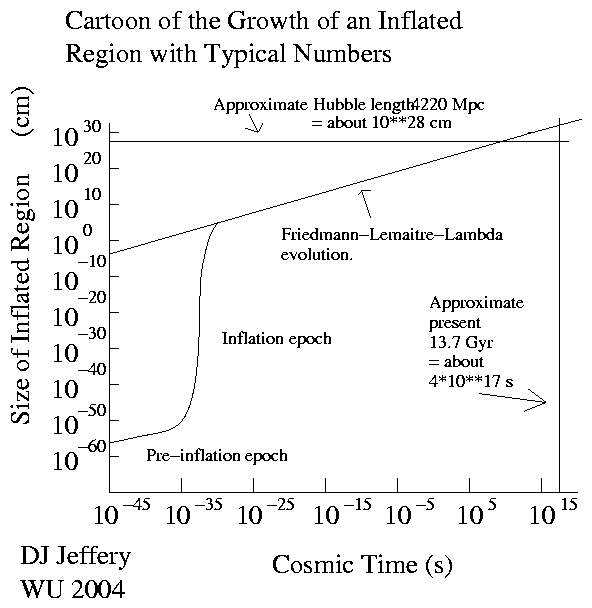
- Image 2 Caption: A cartoon of the inflation super rapid exponential expansion of the inflation region with representative numbers.
- Inflation is typically thought to give an expansion ∼ 60 orders of magnitude and the part that of the inflation region that becomes the observable universe is typically thought to be only ∼ 1 centimeter in scale size ??? at the end of the inflation era (cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero of standard Friedmann equation models).
- The inflation era (cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero of standard Friedmann equation models) happens at lookback time equal to the age of the observable universe = 13.797(23) Gyr (Planck 2018).
When the inflation era ends, the inflation super rapid exponential expansion tracks into the ordinary expansion of the universe of the standard Friedmann-equation (FE) models.
- Note, the inflation super rapid exponential expansion is much like the expansion caused cosmological constant (AKA Lambda, Λ), but is much more rapid, NOT driven by a constant driver, and turns off at the end of the inflation era (cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero of standard Friedmann equation models)
- Now inflation from an infinitesimal speck is unbelievable, but the universe unbelievable too.
However, there are reasons why inflation is plausible (see Wikipedia: Inflation: Motivations) and some evidence (see Wikipedia: Primordial fluctuations; Wikipedia: Inflation: Theory).
- The energy released by the false vacuum decay provides kinetic energy of inflation super rapid exponential expansion and for making fundamental particles (massive particles and massless particles) and heat energy of various kinds.
Note, inflation expansion causes adiabatic cooling, and so the heat energy release is called the reheating.
- The fundamental particles created include eventually, if NOT immediately, photons, leptons, quarks, and probably dark matter particles.
- The inflation era (cosmic time ∼ 10**(-36)--10**(-33) or 10**(-32) s from fiducial time zero of standard Friedmann equation models) is the initial condition for ordinary Big Bang cosmology and, as aforesaid, when the inflation super rapid exponential expansion ends, the expansion tracks into the ordinary expansion of the universe of the standard Friedmann-equation (FE) models as illustrated in Image 2.
Note, the numbers associated with inflation are very uncertain because no one knows the exact properties of the false-vacuum universe or of the inflaton.
Quantum field theorists can only make crude estimates based on what they think should be the appropriate quantum field theory of inflation.
- Note, the fiducial time zero of the standard Friedmann-equation (FE) models is of the Big Bang singularity---which very probably did NOT happen whether inflation is true or NOT.
Recall quantum gravity is believed to prevent the infinite density of the Big Bang singularity. But we have NO established quantum gravity theory to tell us what happens as one approaches Planck density ρ_Planck = c**5/(G**2*ħ) = 5.15500*10**93g/cm**3 where we believe quantum gravity must replace general relativity. General relativity is viewed as the macroscopic scale limit of quantum gravity.
- To emphasize what we said above, in basic inflation we NEED only talk about the inflation region which may be the whole universe.
But in eternal inflation (of which there are many versions, all eternal and infinite), our inflation region is just one pocket universe of which there are infinitely many embedded in a false-vacuum universe.
The pocket universes are usually thought of as having different PHYSICAL CONDITIONS: e.g., initial sizes, densities, cosmological constant values, maybe different fundamental constant values, and maybe some different physics. However, we have to believe that some physics (most importantly general relativity, quantum field theory, theory of everything (TOE), and thermodynamics) is universal or we would have NO physics guidance for eternal inflation.
Eternal inflation itself falls into the category of multiverse which is broader than inflation and itself falls into philosophical cosmology. Philosophical cosmology has its interest, but it can lead to endless speculation.
- Image 2 Caption: A cartoon of the inflation super rapid exponential expansion of the inflation region with representative numbers.
-
Images:
- Credit/Permission: ©
David Jeffery,
2004 / Own work.
Image link: Itself.
- Credit/Permission: ©
David Jeffery,
2004 / Own work.
Image link: Itself.
File: Cosmology file: inflation_paradigm.html.