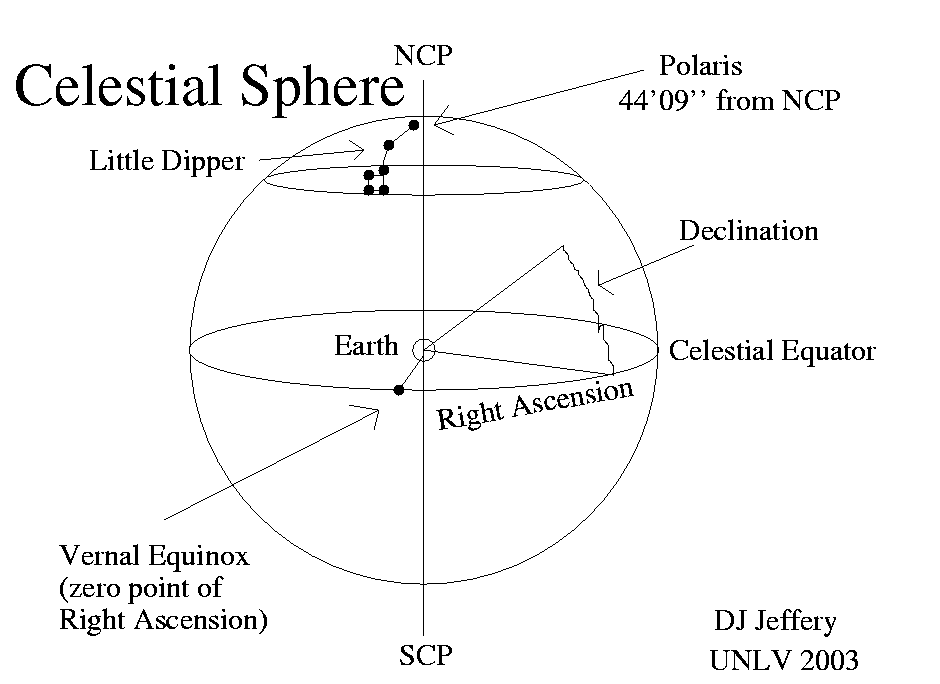
Caption: The equatorial coordinate system is explicated and illustrated.
Features:
- The equatorial coordinate system
is the main
celestial coordinate system
used for locating
astronomical objects on
celestial sphere.
-
The
equatorial coordinate system
is analogous to geographic coordinate system
of longitude and
latitude.
In fact, it is essentially a projection of the geographic coordinates from the Earth's center onto the celestial sphere.
The equatorial coordinate system and the geographic coordinate system are comparably ancient in their earliest versions. Hipparchus (c.190--c.120 BCE) may have invented the first version of the equatorial coordinate system (see Wikipedia: Right ascension: History). Eratosthenes (c.276--c.195 BCE) may have invented the first version of the geographic coordinate system (see Wikipedia: Geographic coordinate system: History).
- The
equatorial coordinate system
coordinate names are different from those of
the
geographic coordinate system.
Right ascension (RA) replaces
longitude and
declination (Dec or δ) replaces
latitude.
Often people identify the equatorial coordinate system by just saying "right ascension and declination" or "RA and Dec" rather than say "equatorial coordinate system".
- The units
of declination are normal:
degrees (°),
arcminutes ('), and
arcseconds (''),
As foreshadowed above, declination is measured is measured north and south of the celestial equator.
But one does NOT say north and south declination.
North is positive declination. South is negative declination.
To be concise: Declination (Dec or δ) is measured from celestial equator in degrees (°), arcminutes (') = 1/60 °, and arcseconds ('') = 1/60 ' = 1/3600 °. Declination to the north/south is counted as positive/negative.
The full range of declination is [-90°,90°]. The south celestial pole (SCP) is at -90° and the north celestial pole (NCP) is at 90°.
- Right ascension is measured
always eastward from the zero-point
the
vernal equinox
on the
celestial equator.
The
vernal equinox
(AKA First Point of Aries)
is
0h RA
(where h stands for
hour
of right ascension: see below).
- The units of
right ascension
are UNIQUE to
right ascension.
To be brief: hours, minutes, and seconds used so that the celestial sphere westward rotates on the celestial axis relative to the Earth 1 hour per hour (more precisely sidereal hour), etc.
- To be detailed:
The angle
units for
right ascension (RA)
are
1 hour RA (h) = 15°,
1 minute RA (m) = 1/4 °,
and
1 second RA (s) = 1/60 m = 1/240 °.
The following table gives their conversions among themselves and to
degrees.
______________________________________________________________________ Table: Conversions for the Angle Units Hours, Minutes, Seconds ______________________________________________________________________ unit hours RA minutes RA seconds RA degrees ______________________________________________________________________ 1 hour RA 1 60 3600 15 1 minute RA 1/60 1 60 1/4 = 0.25 1 second RA 1/3600 1/60 1 1/240 = 0.00625 ______________________________________________________________________
Why are these strange angle units used for right ascension? First note that there is a thing called sidereal time. It and its units are set by the Earth's rotation relative to the observable universe (in older astro-jargon relative to the fixed stars). The Earth rotates westward relative relative to the observable universe at the rates of:
- 24 hours RA per sidereal day.
- 1 hour RA per sidereal hour.
- 1 minute RA per sidereal minute.
- 1 second RA per sidereal second.
The sidereal-time units are all 0.99726958 times their metric system analogs or about 0.3 % shorter. For example, the sidereal day = 86164.0905 s = 1 day - 4 m + 4.0905 s (on average) while the metric day =24 h = 86400 s exactly by definition.
You can see now that the angle units of right ascension were chosen to be the natural units given the nature of sidereal time and its natural units.
The units of right ascension make calculations easy.
For example, if an astronomical object (one unmoving on the celestial sphere) is 3 hours RA east of the meridian, it will transit the meridian in 3 sidereal hours (which is just a bit less than 3 metric hours).
- The full range of right ascension
is from
0 h RA
at the
vernal equinox
to 24
hours RA
back at the
vernal equinox.
Image link: Itself.
Local file: local link: celestial_sphere_003_eqcoord.html.
File: Celestial sphere file: celestial_sphere_003_eqcoord.html.