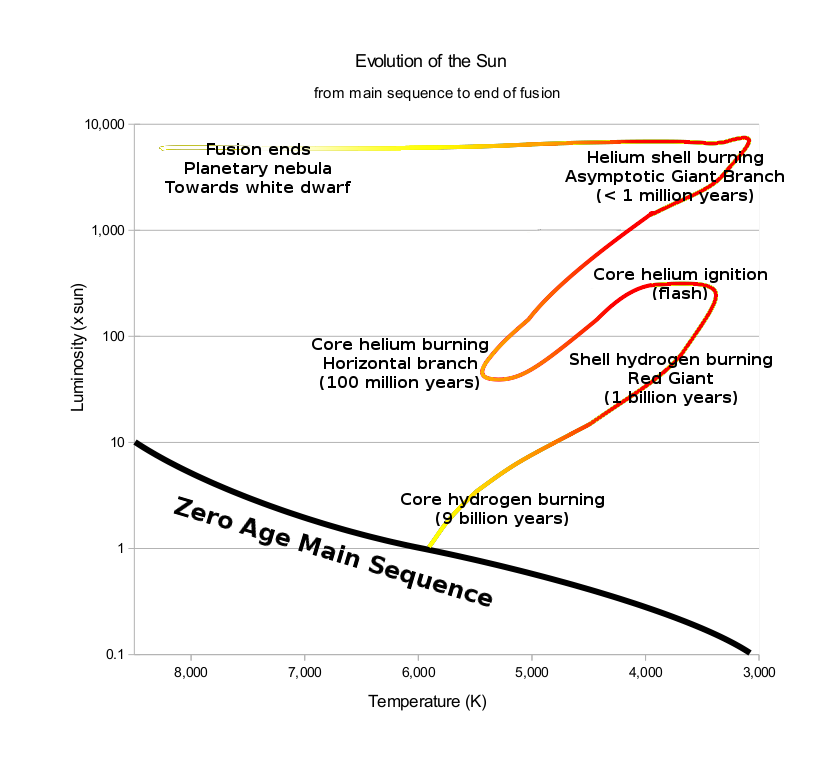
Caption: The stellar evolution on the Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram of a star of stellar mass ∼ 1 solar mass M_☉ = 1.98855(25)*10**30 kg (e.g., the Sun) from the zero-age main sequence (ZAMS) main sequence to the end of nuclear burning lifetime: i.e., the end of its post-main-sequence evolution.
Features:
- The horizontal axis
is photospheric temperature in
kelvins.
Following HR diagram
convention, it is a wrong-way axis with
photospheric temperature increasing
to the left.
Not following
HR diagram
convention, the
horizontal axis
is NOT a
log scale.
- The vertical axis
is a log scale
for luminosity
in units of the
solar luminosity L_☉ = 3.828*10**26 W.
- The stellar evolution phases
shown and some NOT shown on the
HR diagram are:
- zero-age main sequence (ZAMS).
- main sequence.
- subgiant.
- red giant.
- core helium flash.
- horizontal branch.
- asymptotic giant branch.
- planetary nebula.
- white dwarf: The star moves to the blueward to higher temperature then dives to much lower luminosity and becomes a hot young white dwarf. Then it slowly cools moving redward to lower temperature.
- black dwarf: In the far future, billions of years (i.e., gigayears) from now, the white dwarf cools to be a nearly invisible black dwarf. One estimate (which has great uncertainty) gives 10**6 gigayears for a white dwarf to cool to 5 K which will make it very nearly invisibly dark (see Wikipedia: Black dwarf: Formation).
Credit/Permission: ©
User:Lithopsian,
2013 /
Creative Commons
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Image link: Wikipedia:
File:Evolution of a sun-like star.png.
Local file: local link: sun_evolution_hr.html.
File: Sun file:
sun_evolution_hr.html.