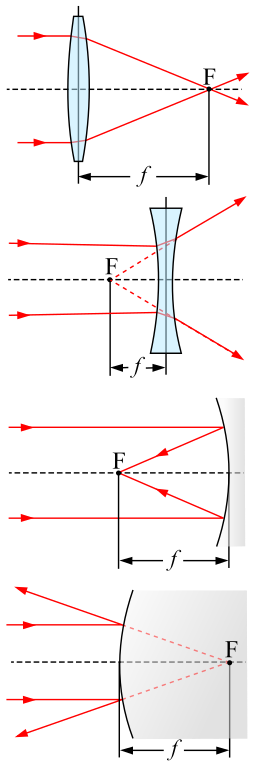
Caption: A schematic diagram illustrating the behavior of lenses and curved mirrors in the limit of Gaussian optics which assumes paraxial approximation: i.e., assumes that light rays make small enough angles to the optical axis that the small angle approximation for the trigonometric functions is valid.
Features:
- Going down the diagram the optical devices are as follows:
converging (biconvex) lens,
diverging (biconcave) lens,
concave mirror,
convex mirror.
- The dashed line is optical axis which is
the symmetry axis of an
optical device.
- F is the focal point (AKA principal focus).
- The two red lines for each case represent a
continuum family of
light rays
parallel
to the optical axis
impacting on the
optical device
and then (converging to)/(diverging from) the
focal point.
- The focal point
is defined by tht (converging to)/(diverging from) behavior it causes
continuum family of
light rays to do.
- f is focal length.
It is the distance from a fiducial point on the
optical axis
(illustrated in the diagram for each case) to the
focal point.
- In the limit of
Gaussian optics,
parallel
light rays
offset by an
angle θ from
the optical axis
will (converge to)/(diverge from)
a point on the focal plane
(a plane
perpendicular to the
optical axis passing through
the focal point)
in a cone whose symmetry axis is offset
from the optical axis
by angle θ likewise.
- In the limit of
Gaussian optics,
simple formulae can be given for
image formation: 1)
for curved mirrors,
the Gaussian mirror equation,
2) for lens,
the thin lens formula.
- The light rays
from a point source of light
that are parallel to
1st order in small
angle offsets are
at optical infinity
by definition.
Such light rays are
treated as exactly parallel
in the imit of
Gaussian optics.
- An extended object at
optical infinity
will create an image on the
focal plane
which can be viewed on a screen or transformed in some other way
(e.g., with an eyepiece
of a telescope).
- The extended object can be treated as a
continuum of
point sources of light
with each point source of light
offset from the others in angle as viewed from
the optical device.
Credit/Permission: ©
User:Henrik,
2008 /
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Image link: Wikimedia Commons.
Local file: local link: optics_lens_curved_mirror.html.
File: Optics file:
optics_lens_curved_mirror.html.