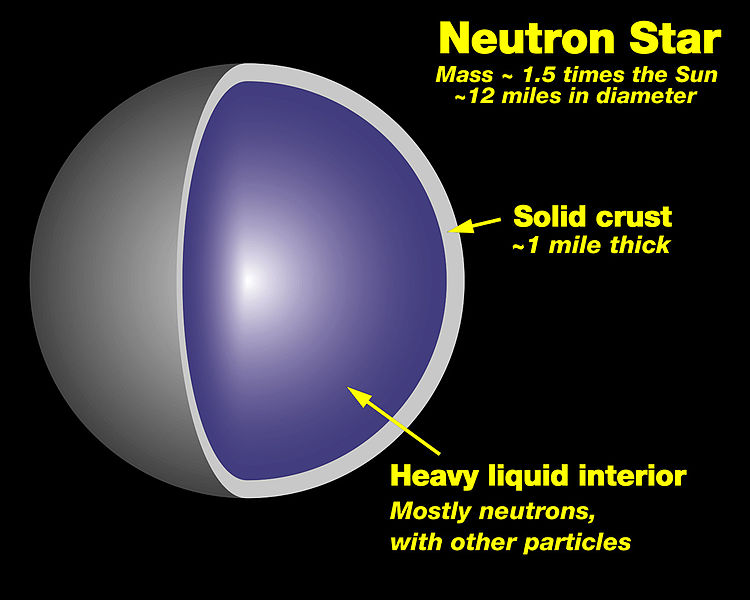
Caption: A very simplified cutaway diagram of a neutron star's structure.
Features:
- A neutron star
is the collapsed core of a large
star
(∼ 8 M_☉ to
20--30 M_☉).
Neutron stars are the compact remnants left by core-collapse supernovae.
- Neutron star masses
are typically 1.5 to 2 M_☉
(see Wikipedia:
Neutron star: Mass and temperature)---2.01 M_☉ is, in fact, the
maximum observed
neutron star mass.
There is a theoretical upper limit to neutron star mass called the Tolman-Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit. As of circa 2017, this limit is thought to be ∼ 2.2 M_☉ based observations. Theoretically, the limit is NOT well constrained, but as is somewhere in the range ∼ 2--3 M_☉. It depends on the behavior of degenerate neutron matter and nuclear matter both of which are NOT fully understood.
Above the Tolman-Oppenheimer-Volkoff limit---whatever it is exactly---the collapse of neutron star to being a black hole is predicted.
- Neutron star radii are of
order 10 kilometers.
Since neutron stars are of order 1.5 to 2 M_☉, they are super dense objects with densities of order 5*10**14 g/cm**3.
Recall liquid water has density almost exactly 1 g/cm**3.
So neutron stars are very exotic objects.
- The surface of
neutron stars is
thought to consist of a
crystal lattice
of atomic nuclei
and free electron gas
(see Wikipedia: Neutron star: Structure).
In deeper layers, free neutrons predominate. Under ordinary conditions free neutrons are unstable to radioactive decay with a half-life of 881.5(15) seconds ≅ 14.67 minutes. But at neutron star densities, neutrons are stabilized.
Much of the interior may be a superfluid of degenerate neutron matter.
More exotic forms of matter are possible too (see Wikipedia: Neutron star: Structure).
- Relatively young
neutron stars
can emit beamed radio radiation
along their
magnetic axis which is the NOT the same as their rotational axis.
The mechanism of beam emission is understood vaguely, but NOT in full detail even
after decades of study
(Wikipedia: Pulsar:
Formation, mechanism, turn off).
The neutron stars that emit beamed radio radiation are called pulsars.
- The beam of radio radiation
sweeps around with the rotation of the
pulsar,
and so periodically will be directed to observers
who detect the
radio pulses---hence
the name
pulsar.
The rotational periods of pulsar are very constant and occur in the range from millseconds to seconds (see Wikipedia: Pulsar).
Pulsars are, in fact, very accurate/precise clocks.
- Pulsars do lose
energy via
their radio radiation
and turn off after 10 to 100 Myr.
Dead pulsars are just rather inert neutron stars in most cases and are rather unobservable.
- There are ∼ 2000 known
neutron stars
in the Milky Way most of which
are pulsars
(see Wikipedia:
Neutron star: Population and distances).
The estimated population in the Milky Way of neutron stars---most of which are rather inert and hard to detect---is ∼ 10**8 (see Wikipedia: Neutron star).
So there is also ∼ 10**8 M_☉ in neutron stars in the Milky Way.
- The Milky Way
mass in
stars
(i.e., its stellar mass) is
estimated to be in the range 4.6*10**10 to 6.4*10**10
M_☉
(see Wikipedia: Milky Way:
Size and mass).
Thus, the fraction of Milky Way stellar mass in neutron stars is only ∼ 2*10**(-3) = 0.2 % which probably makes the neutron star mass insignificant for Milky Way evolution.
- The total Milky Way
mass is
estimated to be in the range 5.8*10**11 to 8.5*10**11
M_☉
(see Wikipedia: Milky Way:
Size and mass).
Most of the Milky Way mass is dark matter which forms the Milky Way dark halo.
Image link: Wikipedia: File:Neutron star cross section.jpg.
Local file: local link: neutron_star_cutaway.html.
File: Neutron star file: neutron_star_cutaway.html.