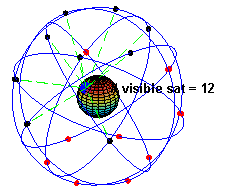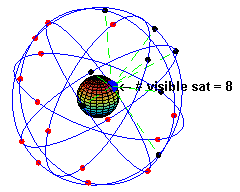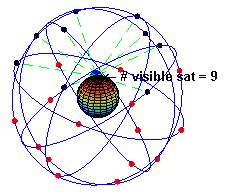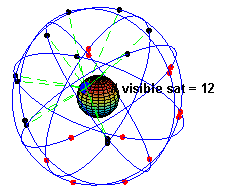
Caption: "An animation illustrating the original design of the Global Positioning System (GPS) Space Segment, with 24 GPS artificial satellites (4 artificial satellites in each of 6 orbits), showing the evolution of the number of visible artificial satellites from a fixed point (45° N) on Earth (considering "visibility" as having direct line of sight)." (Slightly edited.)
Features:
-
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is
how we know where we are
in our time.
- The
black/red
dots are the artificial satellites
above/below the horizon
of the blue
dot (which is a point on Earth at 45° N).
- Actually, this is NOT a good illustration of the
low Earth orbit since the
GPS
artificial satellites
are at orbital radius ∼ 26600 km (altitude ∼ 20200 km)
(see GPS Space Segment),
and so are far above
low Earth orbit.
So they don't rise and set all that frequently. Their orbital periods are about half a sidereal day = 86164.1 s. The SI day = 86400 s (exact by definition).
Note that from Kepler's 3rd law, we obtain the fiducial-value orbital period formula for a test particle (i.e., an astro-body of negligible mass)
p_earth_orbit = 2π/(GM) = (84.4902 ... minutes)*(M/M_⊕)*(R/R_eq_⊕)**(3/2) = (1.40817 ... hours)*(M/M_⊕)*(R/R_eq_⊕)**(3/2) = (0.0586737 ... days)*(M/M_⊕)*(R/R_eq_⊕)**(3/2) ,where M is the mass of the orbited astro-body (assumed to have infinite mass relative to the test particle mass), R is mean orbital radius (AKA semi-major axis of the orbit, gravitational constant G = 6.67408(31)*10**(-11) (MKS units), Earth mass M_⊕ = 5.9722(6)*10**24 kg, and Earth equatorial radius R_eq_⊕ 6378.1370 km. So at orbital radius ∼ 26600 km ≅ 4 R_eq_⊕, we expect an orbital period ∼ 8*0.06 ≅ 0.5 days which agrees with what we said above.
- In the animation,
the GPS
artificial satellites
seem to all rise approximately west and set
approximately east, and so outrace the
eastward
rotation of the Earth or,
from the Earth's perspective,
the daily westward rotation of the
celestial sphere.
The best example of this point is the artificial satellites whose orbital axial tilt is ∼ 30° away from the observer. The near edge of this orbit is the higher edge.
Image link: Wikipedia: File:ConstellationGPS.gif.
Local file: local link: gps_global_positioning_system.html.
File: Earth file: gps_global_positioning_system.html.