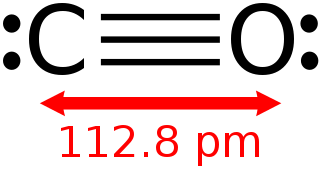
Caption: An ABSTRACT Lewis structure diagram of the carbon monoxide (CO) molecule.
Features:
- "Carbon monoxide (CO)
is a colorless,
odorless,
tasteless
flammable
gas
that is slightly less dense than air
at standard temperature
and pressure (STP).
It is toxic
to animals that use
hemoglobin
as a molecular oxygen (O_2)
carrier (both invertebrate
and vertebrate)
when encountered in concentrations above
about 35 parts per million (ppm)"
(slightly edited from
Wikipedia: Carbon monoxide).
- As the image shows,
carbon monoxide
has a triple bond
using 6
bonding electrons
and each atom has
2 unbonded
valence electrons
(see Wikipedia: Carbon monoxide:
Molecular properties).
The bond length
(i.e., the average
center-to-center distanced of the
atomic nuclei)
is 112.8 picometers (pm)
=1.128 angstroms (Å).
- In the interstellar medium (ISM),
carbon monoxide is the 2nd
most abundant
diatomic molecule
after molecular hydrogen (H_2).
Since molecular hydrogen (H_2)
does NOT radiate strongly,
carbon monoxide
is an important tracer gas
for molecular clouds.
Note the interior of
molecular clouds
can only be observed in the
radio band (fiducial range 3 Hz -- 300 GHz = 0.3 THz, 0.1 cm -- 10**5 km)
and infrared band (fiducial range 0.7 μm -- 0.1 cm)
because of the
opacity
of interstellar dust
in the
ultraviolet band (fiducial range 0.01--0.4 μm)
and
visible band (fiducial range 0.4--0.7 μm
= 4000--7000 Å).
- In fact, carbon monoxide (CO)
is the dominant
radiative line emission cooling
molecule
in molecular clouds despite being
a trace species
(Mark R. Krumholz, 2011,
Physical Processes in Molecular Clouds).
Molecular hydrogen (H_2) despite being
overwhelming dominant in
mass fraction is unimportant
radiative line emission cooling.
- It is NOT surprising that
carbon monoxide is the 2nd
most abundant
diatomic molecule.
Carbon (C) and
oxygen (O)
are the 2nd and 1st most abundant
metals
by mass fraction
in the
cosmic composition
(see solar_composition.html
which is a fiducial
cosmic composition)
and they are both reactive
elements
that easily form
molecules---carbon is forms more compounds
than any other element---it's
"king
of the elements"
(Wikipedia: Carbon).
Image link: Wikimedia Commons: File:Carbon monoxide 2D.svg.
Local file: local link: carbon_monoxide_c_o.html.
File: Atomic file: carbon_monoxide_c_o.html.