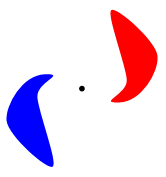
Caption: The blue object is point inverted through the black dot to form the red image---or vice versa mutatis mutandis.
Features:
-
If a point is located at vector R
from an origin, then
a point inversion
locates the image point
vector -R from the origin.
-
A point inversion
can also be regarded as a 180° rotation about a point of every part of
an object.
- Point inversion is physically
realized in
image formation
in most reflector telescopes
and in the
Keplerian telescope
(a refractor telescope).
- It can be corrected for, but most
astronomers don't care---real
astronomers like looking at
point inverted images---so what if it's
tricky to map what you see to what is in the
sky.
- The origin for the point inversion
is the point the
optical axis
of the telescope
(which is the symmetry axis of the
telescope)
becomes when looked end-on.
- The actual observed origin
for the point inversion
is the center of the
field of view (FOV)
of the telescope.
Image link: Wikipedia.
Local file: local link: optics_point_inversion.html.
File: Optics file: optics_point_inversion.html.