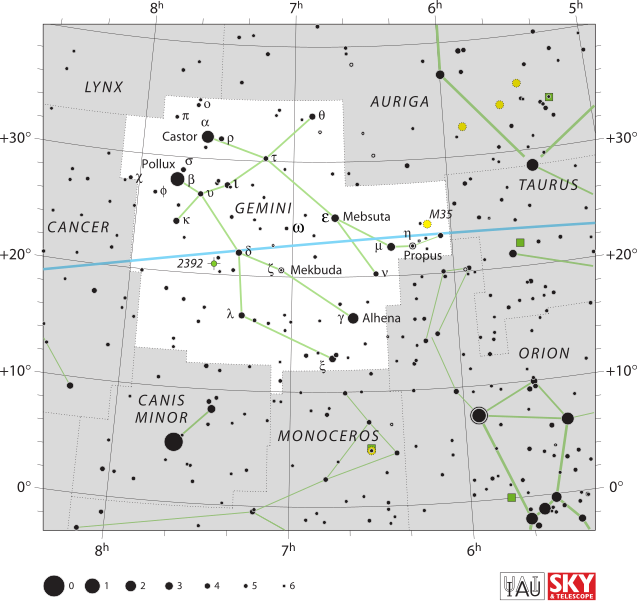
Caption: Constellation Gemini (The Twins) (zodiac symbol ♊) on a sky map of a portion of the celestial sphere.
Features:
- Gemini
is a traditional
zodiac constellation
and is one of the
IAU-defined 88 constellations.
- The
International Astronomical Union (IAU)
is the international organization of
astronomers which has arrogated to itself
the right to name things in the
sky.
- The IAU-defined 88 constellations
are actually patches (i.e., patches of solid angle)
on the
celestial sphere which tile it
completely without overlap.
- All
astronomical objects can be located
by constellation
(in the IAU-defined 88 constellations system): e.g.,
astronomical object X is in
Gemini.
- Gemini
is crossed
by the ecliptic.
- The Sun
moving eastward
(which to the left on the sky map)
on the
ecliptic
(the blue line on
the sky map)
is in constellation
Gemini
(which is NOT the same as
astrological sign Gemini)
in the approximate period
Jun20--Jul20
(∼ 30 days)
(see Wikipedia: Zodiac: Table of Dates).
- The
stars
Castor (α GEM)
and
Pollux (β GEM)
are usually NOT considered a
double star since
they are much farther apart in angle
(∼ 5°)
than the field of view (FOV)
of ordinary telescopes and
are easily seen as 2 stars with
the naked eye.
However, they are an obvious pair on the sky for naked-eye astronomy.
Their angular separation is 4°30'19.53'' at some epoch, maybe the J2000 epoch (see Distance between Pollux and Castor?).
-
Castor---to
naked-eye astronomy a
single star---is
actually
a multiple-star system:
i.e., a small number of stars
that are gravitationally bound.
To be specific, Castor is a sextuple consisting of visual triple (i.e., 3 apparent stars) each of which is spectroscopic binary (a binary system only identifiable as such via spectroscopy and the Doppler effect).
The two brightest members of the visual triple constitute a double star in small telescope observation: i.e., Castor A and Castor B (see Wikipedia: Castor: Physical properties) which are separated by 4.87'' in 2013 (see Observer's Handbook, Royal Astronomical Society of Canada).
It takes excellent seeing for near the Las Vegas Strip (∼ 4'') to resolve Castor A and Castor B.
Image link: Wikimedia Commons.
Local file: local link: iau_gemini.html.
File: Constellation file: iau_gemini.html.