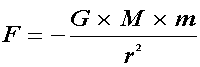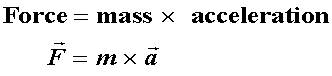- Need:
- 1.Relative distances of planets from the sun
(get from trigonometry)
- 2. Value of astronomical unit
- To measure AU: measure parallax angle of planet and
distance between observers on earth
- Get distance to any planet, if distance from sun in AU is known and get value of 1 AU
- First attempt to measure 1 AU, 1672 - Mars
- Now use radar - very accurate
Newtonian Gravitation
- Isaac Newton (1642 - 1727)
- Every body in universe attracts every other with a force
depending on masses and distance between bodies.
Law of Gravity:
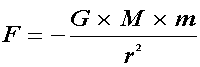
- Where,
- G: gravitational constant
- M: mass of larger body
- m: mass of smaller body
- r: distance between bodies
- Mass: amount of material in body
- Weight: depends on gravitational force acting on body
Newton's Laws:
- 1. Newton's First Law: Body in motion remains in motion unless acted on by an outside force
- Force: Can cause change in speed, direction or both.
- Velocity: Speed in a particular direction.
- Acceleration:Change in velocity.
- 2. Newton's Second Law:
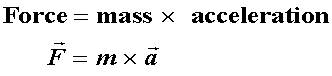
| mass, m |
acceleration, a |
force, F |
| m = 1.5 |
a = 2 |
F = 3 |
| m = 1.5 |
a = 4 |
F = 6 |
- 3. Newton's Third Law: Every action has an
equal and opposite reaction.
- The acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects in a particular gravitational field.
- Acceleration due to gravity at earth's surface:
| seconds |
speed (ft/sec) |
speed (m/sec) |
| 1 |
32 |
9.8 |
| 2 |
64 |
19.6 |
| 3 |
96 |
29.4 |
| 4 |
128 |
39.2 |
| 5 |
160 |
49.0 |
- g: acceleration due to gravity, 32 ft/s/s, or 9.8 m/s/s
Orbits
- Sensation of weight - resisting force of gravity
- Falling freely - not resisting gravity - feel 'weightless' BUT
GRAVITY IS STILL THERE
- Inside closed spaceship - cannot differentiate free fall near a planet or 'floating around' far from all sources of gravity (masses)
- Escape velocity - smallest velocity required to leave earth (or any other body) and not return
- Circular velocity - velocity required to orbit earth (or any other body) at a constant altitude, i.e. in a circular
orbit. Ignoring air resistance, will orbit indefinitely.
- Speeds greater than circular velocity produce elliptical
orbits.
- Escape velocity produces parabolic orbits
- Speeds greater than escape velocity produce hyperbolic
orbits.

Einstein, Gravity, and Relativity
- Velocity of electromagnetic radiation is constant,
regardless of observer's velocity relative to source.
(Michelson - Morley experiment)
- E = mc2
- Gravity as a distortion of space near massive bodies
- The more massive the body, the greater the
distortion
- Space and time linked in a 4 dimensional description of
the universe (space-time) and how things move in it
- Confirmation of General Relativity:
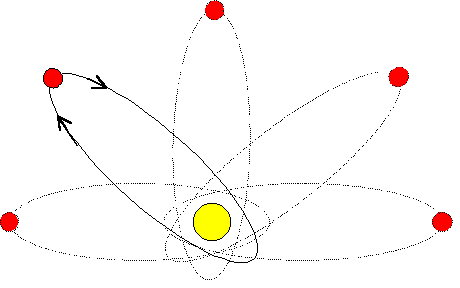
- 1. Precession of Mercury's orbit:
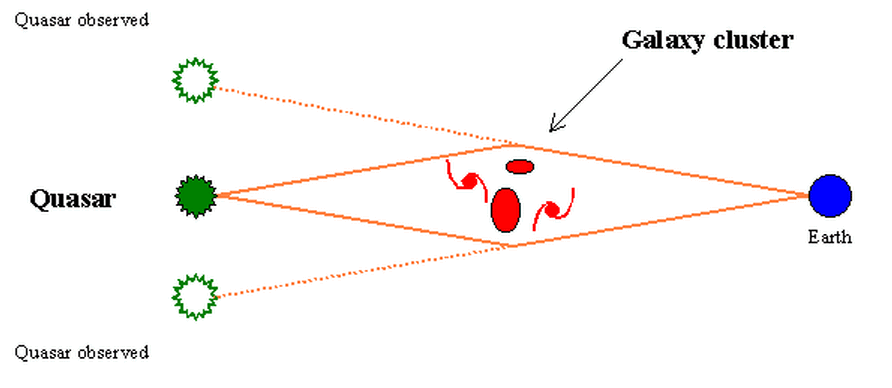
- 2. Deflection of starlight near large masses - gravitational lenses:

- All tested predictions of General Relativity confirmed thus far.
- Under everyday circumstances, Newton's gravity
and Einstein's relativity give same result.
- Relativity must be used
- 1.at velocities approaching speed of
electromagnetic radiation ("light")
- 2. when very strong gravitational fields are present
- 3. when considering the large-scale universe.
Prof. Donna Weistrop
University of Nevada, Las Vegas